AI Geopolitics and Key Actors: The New Global Power Struggle
The Battle for AI Supremacy: More Than Just Technology
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a niche field of computer science; it has become the central arena for 21st-century geopolitics. The development and control of AI technologies are reshaping global power dynamics, economic competitiveness, and national security. This AI geopolitics landscape is defined by a complex interplay between nation-states pursuing strategic dominance and corporate giants wielding unprecedented influence.
This analysis breaks down the key actors in AI—from the fierce US-China rivalry and the EU's regulatory approach to the dominance of Big Tech and the rising global players. Understanding these forces is crucial for comprehending the future of global economics, security, and governance.
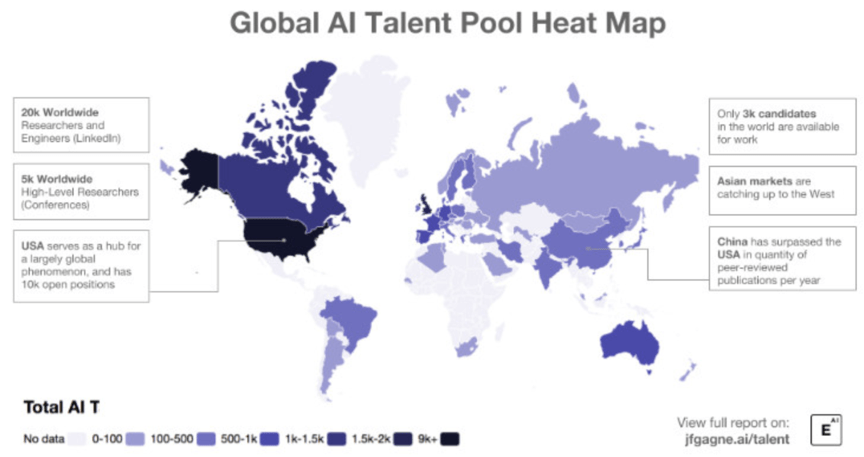
The Nation-State Actors: A Tripolar World
The global AI race is primarily a contest between three distinct models of technological development and governance: the market-driven US approach, the state-led Chinese model, and the rules-based European framework.
1. United States: The Incumbent Power
The US maintains its lead through a powerful synergy between its world-leading tech industry, top-tier academic institutions, and significant defense investment. Its strategy emphasizes private sector innovation with government support through initiatives like the CHIPS and Science Act and R&D funding from agencies like DARPA and IARPA. Learn about the US approach to AI rights and safety.
Key Advantages: Dominance in foundational models (OpenAI, Anthropic), venture capital, top AI talent, and control over key semiconductor IP and software ecosystems.
2. China: The Strategic Challenger
China's approach is state-directed, ambitious, and holistic. Guided by its "Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan", it aims to become the world's primary AI innovation center by 2030. Its model leverages massive state funding, a vast domestic market for data generation, and a national commitment to technological self-reliance. Analyze China's AI regulatory framework.
Key Advantages: Massive data availability, strong government support and funding, rapid implementation, and leading companies like Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent (BAT).
3. European Union: The Regulatory Power
The EU, while not a leader in developing cutting-edge AI models, is positioning itself as the global standard-setter for ethical and trustworthy AI. The landmark AI Act is the world's first comprehensive AI law, creating a risk-based regulatory framework. This "Brussels Effect" could see EU standards de facto adopted globally. Read the EU Parliament's guide to the AI Act.
Key Advantages: Regulatory influence, strong research in ethics and explainable AI, and industrial strength in specific applications (e.g., manufacturing, automotive).
Other Notable Players: The “Sharp Middle Powers”
- United Kingdom: Aims to be a global leader in AI safety, hosting the first AI Safety Summit and establishing the AI Safety Institute. UK AI Regulation White Paper.
- India: Leveraging its vast IT talent pool and digital public infrastructure for AI development focused on societal needs. IndiaAI Initiative.
- United Arab Emirates & Saudi Arabia: Using sovereign wealth funds to invest heavily in AI and position themselves as hubs for the Global South. UAE's National AI Strategy.
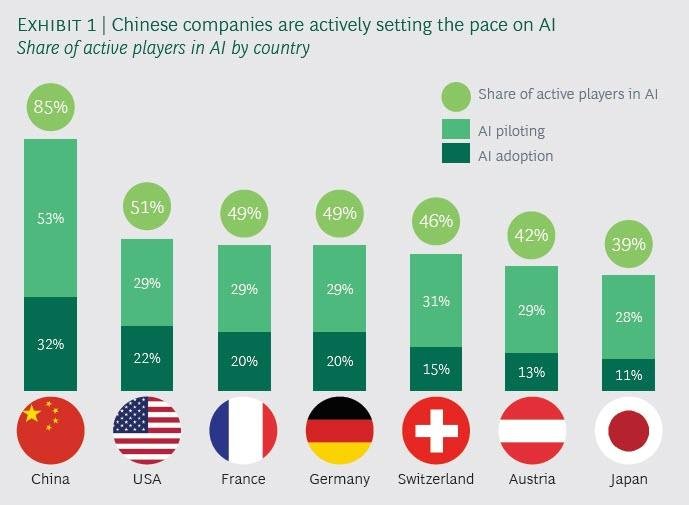
The Corporate Actors: The Titans of Tech
A handful of US and Chinese companies, often referred to as the "AI Majors," control a disproportionate share of the talent, data, and computational resources required for advanced AI. Their influence rivals that of mid-sized nations.
The US “Magnificent Seven” and Beyond
- Microsoft (OpenAI): A dominant force through its partnership with OpenAI, integrating AI across its Azure cloud and software empire.
- Google (DeepMind): A pioneer in AI research with DeepMind and a leader in AI-powered search and cloud services.
- Meta: Focuses on open-source AI (Llama models) and integrating AI into its social media and metaverse platforms.
- Amazon & NVIDIA: Amazon dominates AI-as-a-service (AWS), while NVIDIA's GPUs are the essential "picks and shovels" of the AI gold rush.
The Chinese Champions
- Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent (BAT): These internet giants are at the forefront of China's AI efforts, from autonomous driving to cloud computing and large language models for the Chinese language.
- Huawei & SenseTime: Focus on AI hardware (chips, servers) and computer vision applications, respectively.
The power of these corporations raises critical questions about AI governance and accountability. Their decisions on model deployment, safety, and open-sourcing have global consequences. Explore the debate on corporate power in AI.
Geopolitical Flashpoints and Strategic Dimensions
The AI competition manifests in several critical, interconnected domains that are sources of both innovation and tension.
1. The Semiconductor Supply Chain
AI development is inextricably linked to advanced computing hardware. The US-led export controls on high-end AI chips to China represent a pivotal move in the tech war, aiming to slow China's progress by restricting its access to critical technology. This has forced China to accelerate its own chip industry, exemplified by Huawei's SMIC-manufactured Kirin chips. CSIS analysis of the semiconductor tech war.
2. The Race for Talent
AI is a human capital-intensive field. A fierce global battle for top AI researchers and engineers is underway. The US has historically benefited from a "brain drain," attracting global talent to its universities and companies. China is now aggressively working to retain its own talent and attract international experts.
3. Military AI and Lethal Autonomous Weapons (LAWS)
The integration of AI into military systems is perhaps the most contentious issue. The development of LAWS, or "killer robots," raises profound ethical and security questions, potentially leading to a new global arms race and destabilizing crisis dynamics. International talks at the UN have so far failed to establish a binding treaty. Human Rights Watch on the urgent need for regulation.
4. The Battle for Standards and Norms
This is a battle over the soul of the digital future. Will the global internet be governed by a US-modeled vision of a relatively open web? A Chinese-modeled vision of cyber sovereignty and state control? Or an EU-modeled vision based on human-centric regulation and privacy? The outcome of this battle will determine how AI technologies are used globally for decades to come.
Future Outlook: Cooperation, Conflict, or Fragmentation?
The most likely future is not a single winner-takes-all outcome but a period of continued competition and potential fragmentation, often called a "Splinternet" or "tech decoupling."
- Scenario 1: Fragmented Ecosystems: Separate US and Chinese tech stacks emerge, with other nations forced to choose sides or navigate a complex, bifurcated digital world.
- Scenario 2: Managed Competition: Major powers establish "guardrails" and limited cooperation on global AI safety risks while competing economically and militarily.
- Scenario 3: Arms Race Escalation: A failure to establish norms leads to a rapid and dangerous militarization of AI, increasing the risk of conflict.
The path taken will depend on the choices made by the key actors in AI today. The need for international dialogue, exemplified by forums like the Bletchley Park and Seoul AI Safety Summits, has never been greater. Understanding the goals of international AI Safety Summits.
Conclusion: Navigating the New AI World Order
The geopolitics of AI is a multifaceted struggle encompassing technology, economics, ethics, and military power. The interplay between nation-states like the US, China, and the EU, and corporate giants like Microsoft, Google, and Baidu, will define the trajectory of this transformative technology.
There is no single "right" path. Each model—American innovation, Chinese state direction, European regulation—offers strengths and faces significant challenges. The central question for the future is whether these competing systems can find a way to manage their competition and cooperate on mitigating existential risks, or whether the world will split into incompatible and hostile AI blocs. Understanding these dynamics is the first step toward navigating this new, uncertain world.




